Brake noise is one of the biggest reason a driver goes to the maintanance. It can be a complex problem and often difficult to solve. But FRENDI is there for convenience.
WHAT IS BRAKE SOUND?
Brake noise is caused by vibration in the wheel at the rear of the vehicle, a part located between the tire and the chassis link. The brake pad is often seen as the cause for the noise, but it can come from anything from the wheel bearing to the ball joint. Some vibration in the brake system is normal, but usually not loud enough to be heard.
A. SOUND TYPES
B. WEAR SURFACES
C. PREVENT SOUND PROBLEMS
A. TYPES OF SOUND DRIVERS ENCOUNTER
LOW FREQUENCY VIBRATIONS

EXPLANATION:
Deep sounds below 300 Hz frequency.
REASONS
• Weak tolerance (weak mounting on the hub or excessive disc thickness difference).
• Disc damage
SOLUTION:
Replace the disc and clean and lubricate all surfaces of the brake assembly according to the vehicle manufacturer's instructions.
MEDIUM FREQUENCY VIBRATIONS – SqueakIng

EXPLANATION:
Sound in the frequency range 300 - 5000 Hz.
REASONS:
- The movement of the caliper piston by being stuck,
- The brake disc working surface is not flat.
- Brake pad placement failures,
- misalignment of the anti-sound fasteners (as shims).
- Too much wear in brake disc thickness.

SOLUTION:
- Clean and lubricate the caliper components,
- Make sure the flatness of the brake disc is within the tolerance range ( after being placed on the hub) of 0.1 mm.
- Clean the hub surface, machine the brake disc surface,
- Replace the brake disc and make sure the pads, shims and accessories are properly installed.
- Consider reducing sound intensity with shims or use brake pads with noise reduction.
HIGH FREQUENCY VIBRATIONS –
EXPLANATION:
Frequency sound higher than 5 kHz.
REASONS:
The most common squealing cause is molecular vibration in the friction material as it is applied to the brake disc.

SOLUTION:
Replace the brake pad assembly. Also, check that the accessories (e.g. caliper clips) are the correct accessories and fitted properly.
VERY HIGH FREQUENCY VIBRATIONS

EXPLANATION:
Sound with a frequency than 12 kHz, greater than the upper limit of human hearing.
B. FRICTION SURFACES GIVE IMPORTANT TIPS
The appearance of friction surfaces is one of the typical signs of the cause of sound problems. Jack up the vehicle, remove the pads and inspect the wear surfaces to analyze potential problems.
SIGNS AND SOLUTIONS
CONICAL PADS
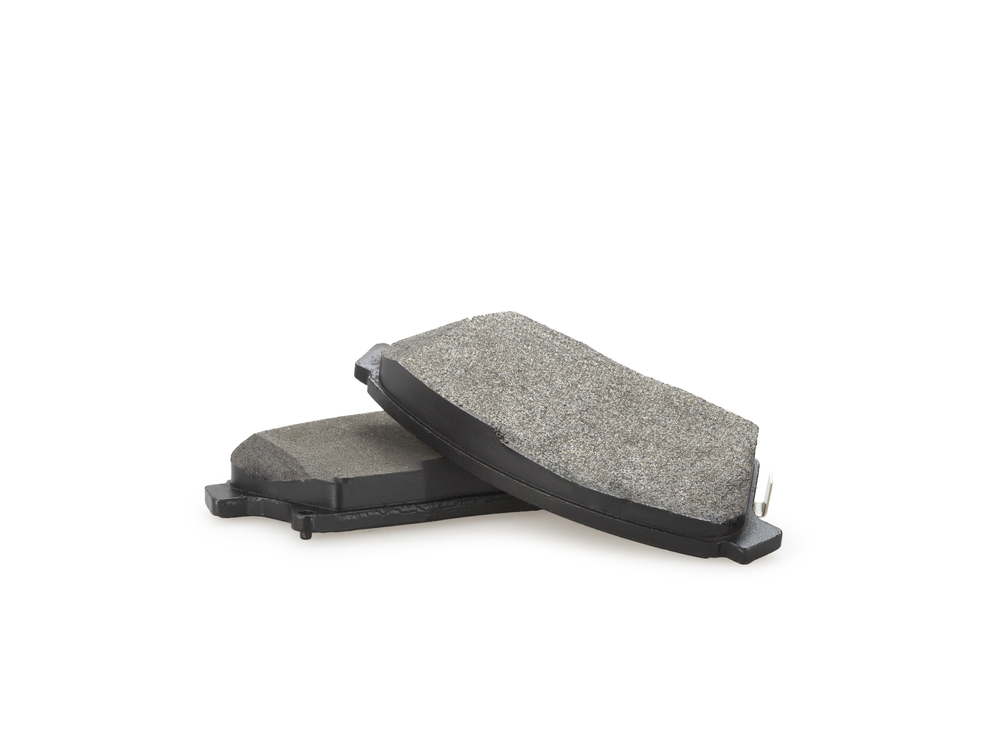

APPEARANCE: Uneven wear, tapered pads
CAUSES: Bad caliper, jammed caliper slides, excessive caliper space
EFFECTS: Earlier pad wear, unbalanced brake pressure, noise
SOLUTION: Replace pad set, service and maintain caliper
UNBALANCED WEAR
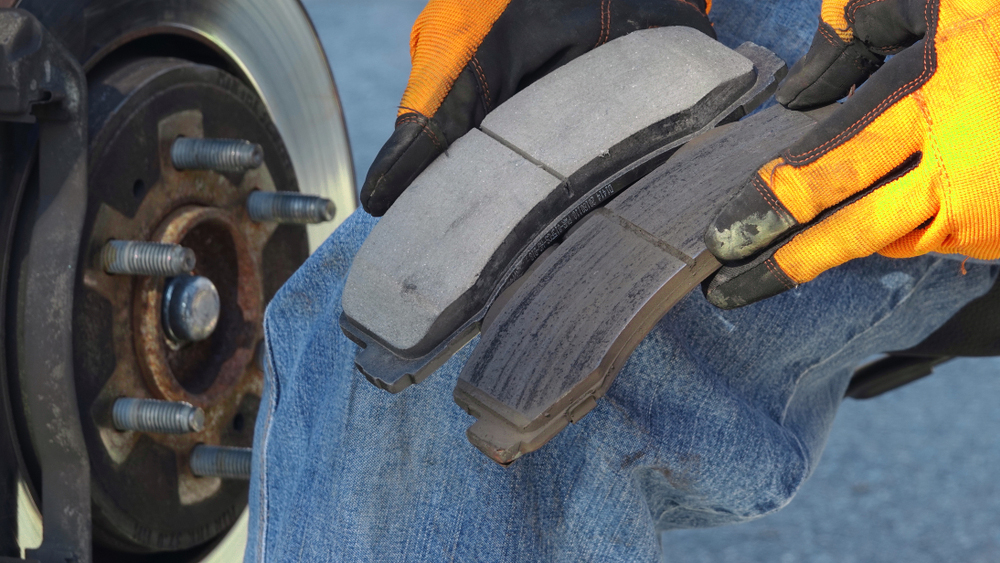

APPEARANCE: Uneven wear on the pad surface
CAUSES: Unevenly worn brake disc (worn gasket visible on disc)
EFFECTS: Squeaking and vibration, earlier pad wear
SOLUTION: Replace brake discs and pads
UNBALANCED WEAR ON THE AXLE
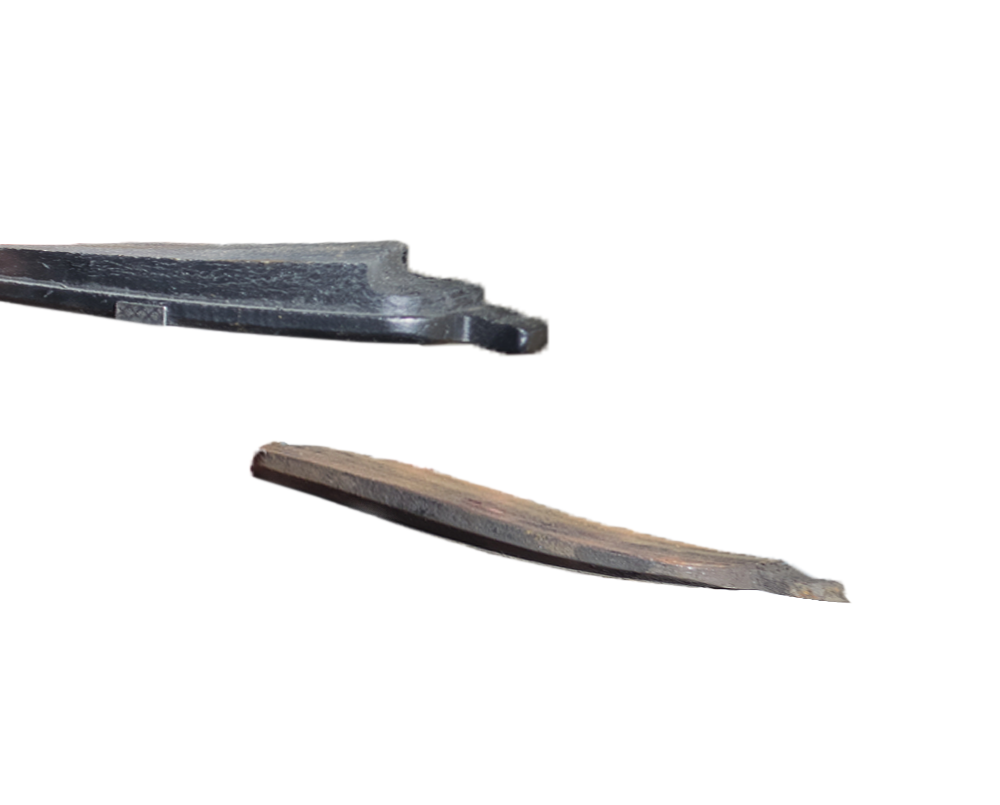

APPEARANCE: One or more worn linings on the axle assembly
CAUSES: Stuck in caliper guide pins or piston
EFFECTS: The vehicle pulls to one side during braking, uneven and rapid wear on the pads, squeaking and vibration
SOLUTION: Service all caliper slides and pistons, replace pads. Check Brake Discs
DAMAGED BACK PLATE
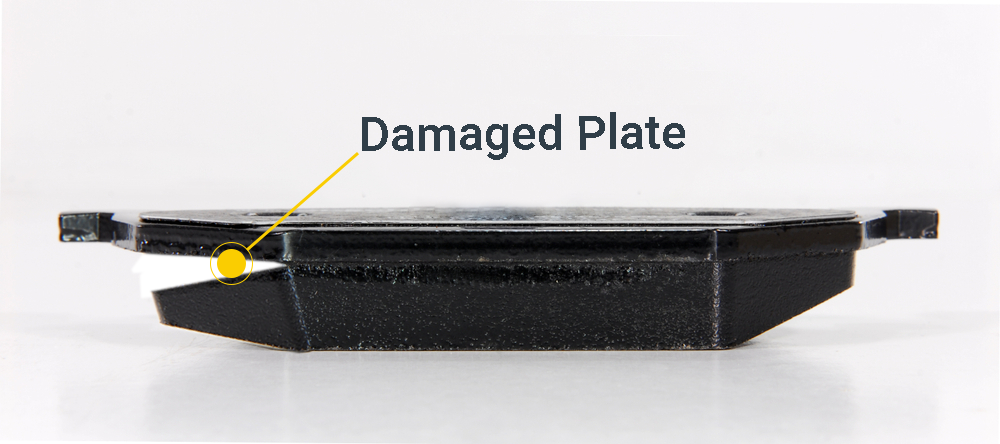
APPEARANCE: Damaged backing plate
CAUSE: Incorrect assembly, excessive force during assembly
EFFECT: Inefficient braking, uneven wear, noise and vibration
SOLUTION: Replace the entire brake pad assembly
DAMAGE TO THE PISTONS
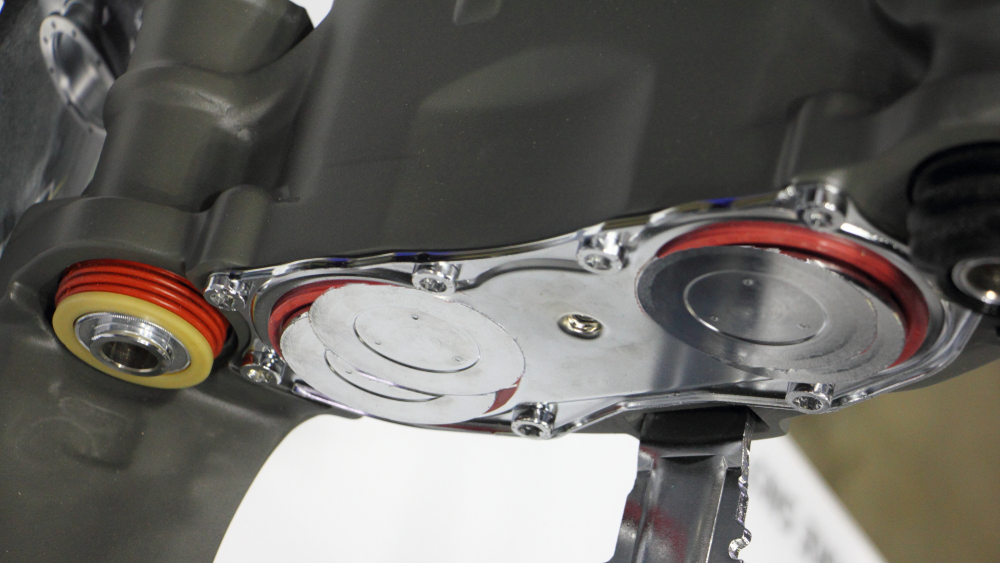

APPEARANCE: Anti-noise properties caused by the piston (plastic coating / shim)
CAUSE: Piston not fully retracted, heavy braking
EFFECT: Overheating, noise
C. PREVENT SOUND PROBLEMS
The easiest way to avoid problems is to have the brake pads and caliper installed correctly.
Suggestion fort he correct assembly:
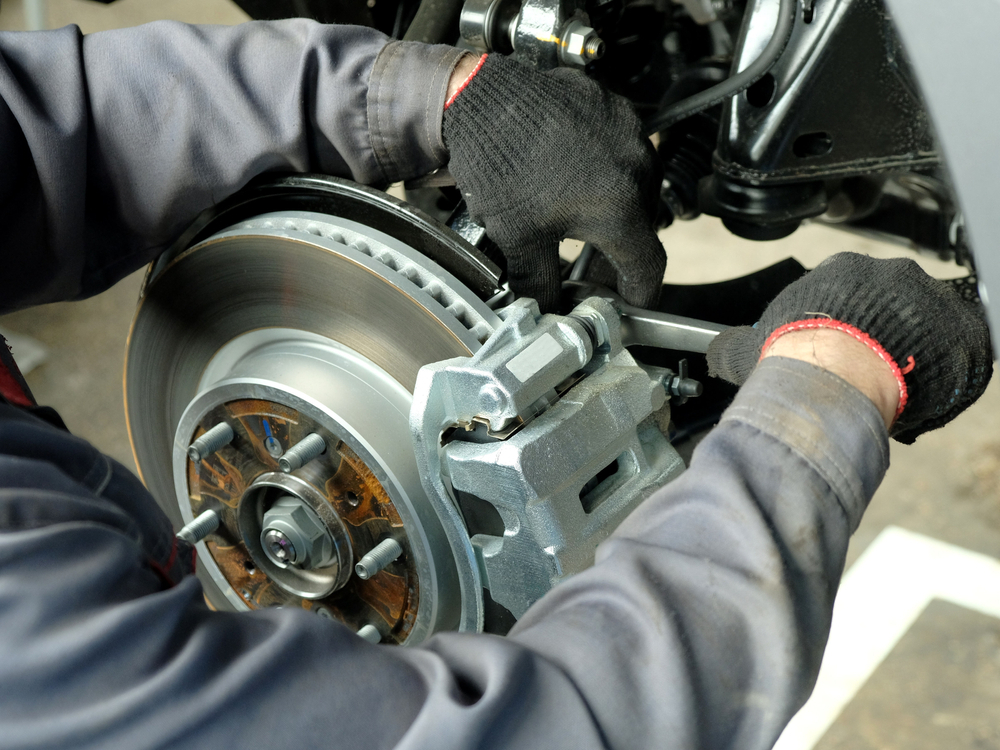

• Remove and clean all caliper slides and pins.
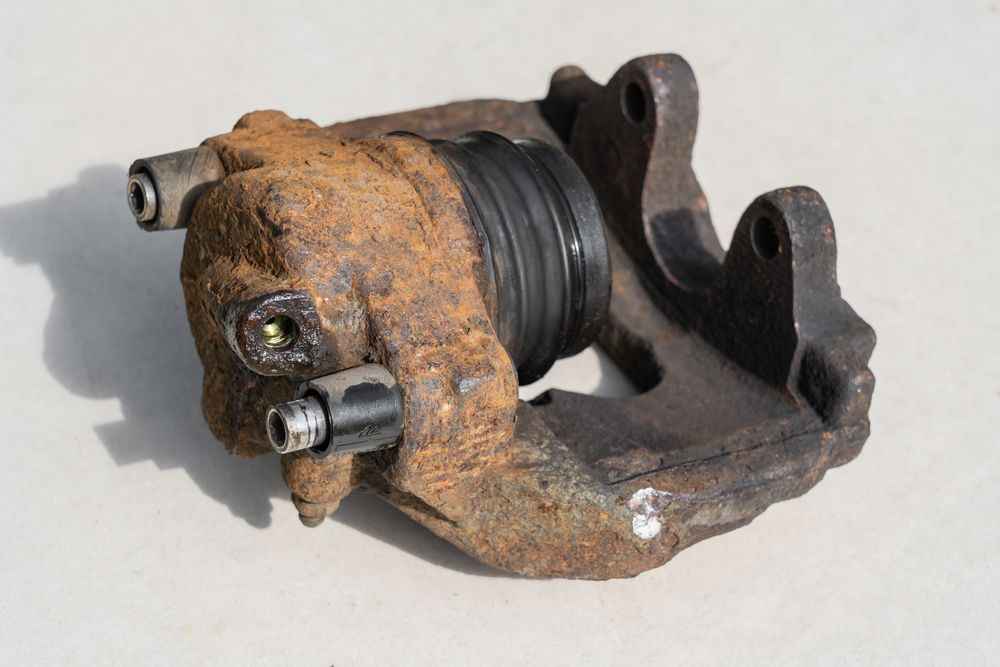

• In case of heavy rust or harmful substances, sandpaper can be used only on the caliper and pad feet.
Note: if the caliper does not slide easily, this can cause tapering of the pads or uneven wear on the axle, which will cause squeaking and vibration.
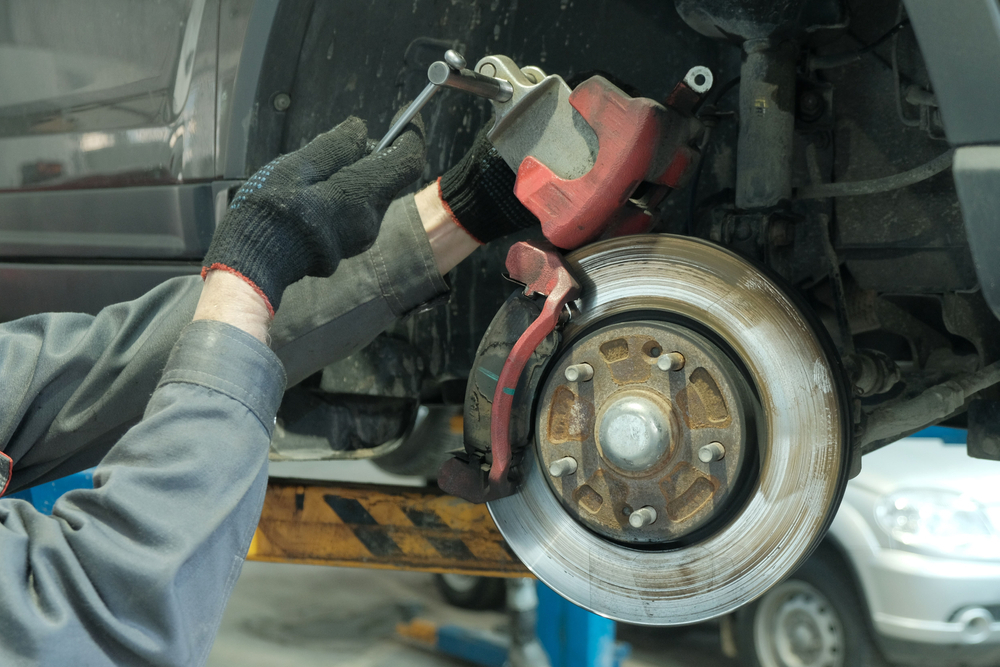

• The pin must be properly lubricated to ensure that it moves freely and does not run into the caliper body. Also check the condition of the plastic shoes of the sliding pin to prevent water from entering.
Note: if the pins are not lubricated, they may cling causing tapered wear and sound problems.
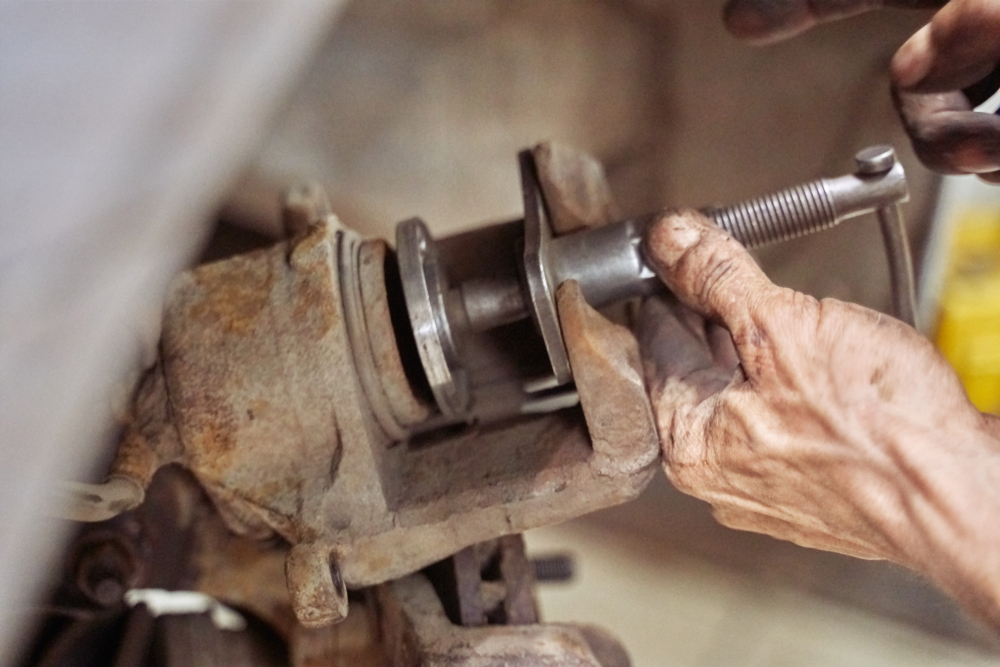

• Check that the piston moves freely and is fully pulled. This procedure is necessary to prevent damage to the shim or plastic coating.

• Check that the brake pads fit freely and easily into the caliper holders.

• If necessary, clean the edges of the brake pads for roughness.
Note: if the pad inside the bracket does not move freely, there may be continued light contact with the discs, causing squeaking and tapering of the pads or uneven wear on the axle.

• In certain special cases (eg an old and rusty caliper), it is recommended to lightly lubricate the metal backplate and slides with copper grease according to the vehicle manufacturer's instructions.
Note: be careful that grease NEVER touches the friction material.

• Put wear indicators on the brake pads where appropriate.
• Screw in the caliper fixing bolts.
• Replace the threadlocker bolts with new ones.

• Follow the correct tightening torque and sequence recommendations.
• With the brake caliper installed, depress the brake pedal one-third.
• Make sure the brake is working properly, including the pad retraction.
• Reinstall the wheel. If it turns freely, the vehicle is ready for traffic.

