What is Main Brake Cylinder and What Does It Do? (Duty of Brake Central Pump)
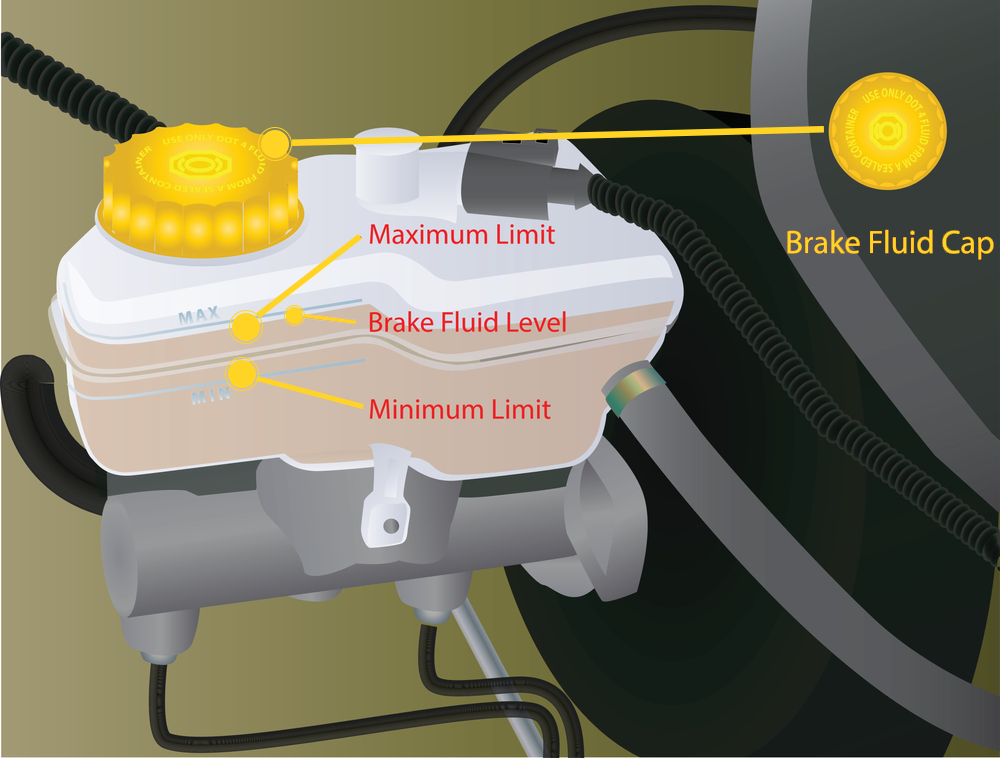
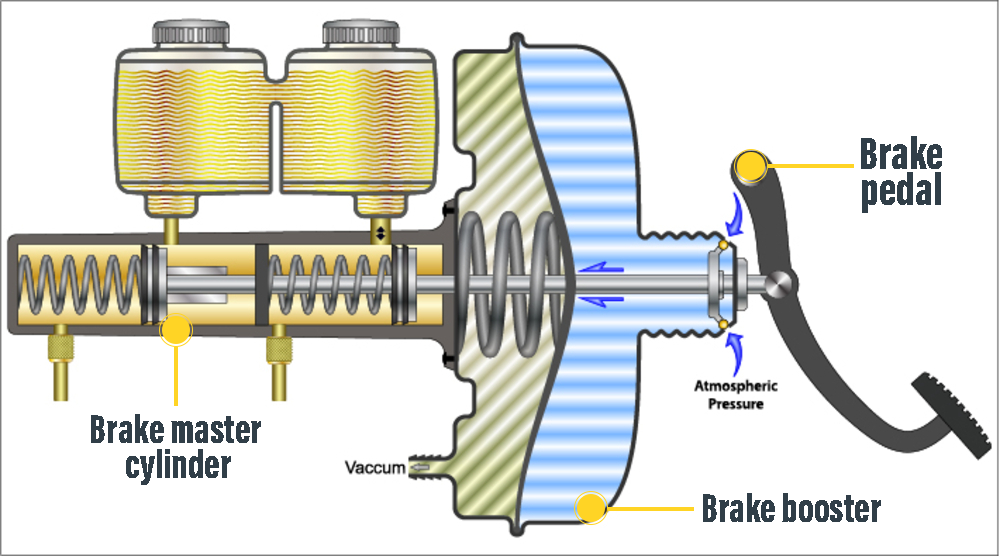
Brake master cylinder (brake center pump) is the part that converts the force applied by the driver to the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure and sends it to the wheel brake mechanisms. The hydraulic pressure created in the brake master cylinder is applied to the calipers in disc brakes; in drum brakes, it is sent to the wheel brake cylinder. The brake center pump (cylinder) is located just in front of the brake booster and the brake fluid reservoir box is located above it. Brake main cylinder takes the brake fluid it needs from here and the hydraulic coming back from the brake line returns to this reservoir.
What are the Functions of the Brake Main Cylinder?
*To ensure rapid build up of hydraulic pressure in the brake line,
*Balancing the volume changes in the brake hydraulic fluid (thanks to the brake fluid reservoir tank) due to temperature differences,
*To complete the brake fluid in the brake line (cause of the brake fluid reservoir) so that there is no gap in the brakes due to the wear of the brake pads.
Parts and Structure of Brake Master Cylinder
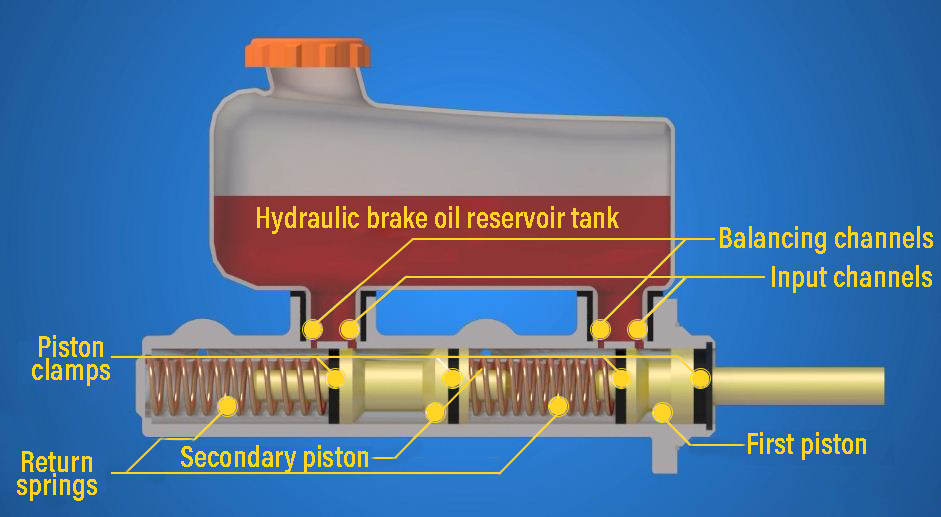
There are two pistons (tandem cylinder) inside the brake master cylinder (brake center pump), thanks to these two pistons, two separate brake line outputs are obtained from the brake center. The brake hydraulic oil tank is mounted on the brake master cylinder, the brake hydraulic oil tank meets the hydraulic oil requirement in the system, and the brake oil returns to this tank when braking is finished. The brake fluid reservoir is also divided into two separate compartments inside, so that in case of a leak in one of the brake lines, it can continue to supply oil for the other brake line. There is also an oil level sensor in the brake fluid reservoir.
The parts of the main brake cylinder are:
*Primary piston and piston return spring
*Second piston and piston return spring
*Piston seals – seals (sealing elements)
*Brake hydraulic oil reservoir tank
*Brake hydraulic oil level sensor
Working Principle of Main Brake Center (How Does Main Brake Work?)
Normal Position (No Brake Pedal)
In this case, the passage channels from the brake fluid reservoir tank to the main brake cylinder are open.
Two return springs inside the cylinder have pushed the pistons back. Two passage channels are connected from the brake fluid reservoir to both chambers in the cylinder. The larger channel is called “inlet channel – inlet hole”, it provides oil reinforcement from the hydraulic tank to the cylinder. The second and narrower channel is called “balancing channel – balancing hole”, According to the pressure change in the brake line, brake oil is sent or returned from the reservoir tank.
Operating Position (Brake Pedal Depressed):
When a liquid in a closed resorvoir is compressed by a piston (liquids are incompressible), pressure is created in the liquid and this pressure is applied equally to every surface in the resorvoir. In the brake master cylinder, the driver presses the brake pedal, the pedal push rod is transferred to the brake servo, and this thrust force is increased in the brake servo. The push rod at the output of the brake booster pushes the first piston in the main brake cylinder forward, while the piston moves forward, it creates pressure in the brake oil in the chamber in front of it, this pressure both pushes the second piston in front of it forward and creates the hydraulic pressure sent to the 1st brake line. The second piston pushed forward by the first piston also moves forward, creating pressure in the brake fluid in the chamber in front of it. This pressure is sent to the 2nd brake line. Thus, hydraulic oil pressure is sent to the caliper piston in the wheels or the brake cylinder in the drum and braking is done.
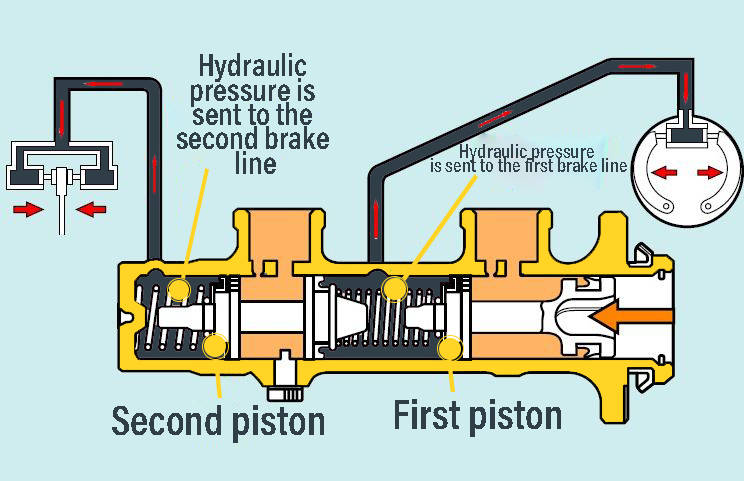
(Main Brake Cylinder Operating position-brake pedal depressed)
Control valves are located in the output lines of the brake center pump (Main cylinder). These control valves allow passage from the brake center pump to the wheels, but on the return, that is, on the return from the wheels to the brake center when the brake pedal is released, they are closed when the pressure drops below a certain value, so that when the brake pedal is not depressed, the hydraulic oil will be ready to kept on hold at a certain pressure in the brake line. In the ABS brake system, the hydraulic pressure created by the brake master cylinder is sent to the ABS hydraulic module and distributed to the wheels from this hydraulic module.
When Brake Pedal Released:
The driver takes his foot off the brake pedal and the thrust applied to the main brake cylinder piston is eliminated. Pressurized hydraulic brake oil is no longer sent to the brake system. The return springs in the brake master cylinder push the pistons back (to their previous position). Pressurized brake oil in the brake line returns to the reservoir tank.
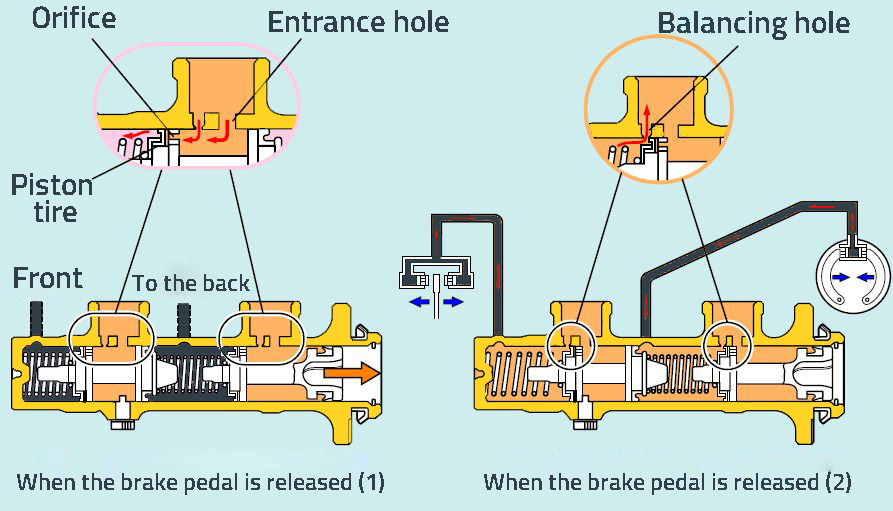
(Return of hydraulic oil when the brake pedal is released)
When the brake pedal is released, the balancing channel performs an important function. When the brake pedal is released, the pistons retract quickly, but the pressurized brake oil in the system cannot return as quickly. In this case, a vacuum (low pressure) is formed in the master cylinder as a result of the rapid volume increase in the chambers in front of the pistons. This channel balances the vacuum created in the chamber as a result of the return springs pushing the piston back when the brake pedal is released, by sending hydraulic oil there. When the piston returns to its normal position, the pressurized hydraulic oil still present in the brake line returns to the reservoir tank through this channel.
In addition, when the brake hydraulic oil, whose volume changes with temperature, expands, it flows back to the reservoir box from the balancing channel and spontaneous pressure build-up in the cylinder due to the temperature effect is prevented.
Brake Hydraulic Circuit Types
What happens if the brake blows? What happens if the brake hose leaks fluid?Will the braking continue? The brake hydraulic lines are split so that the brake system can continue to work if there is any leakage in the brake system. Two separate hydraulic pressure lines exit the brake master cylinder;
a) Parallel Brake Line: One line is connected to the front wheels and the other line is connected to the rear wheels, this is called the parallel brake line. When the front wheel brake hoses leak, the rear brake continues to hold because the rear wheel brakes are supplied from a separate line. Or vice versa, when the rear brakes blow, the front brakes continue to hold. Only the braking of the rear wheels creates very weak and unbalanced braking, or the braking of only the front wheels impairs the vehicle's balance-road handling; this type of brake coupling system is not used today.
b)Cross Brake Line: In this system, the two hydraulic lines coming out of the brake center are diagonally; separated and connected as left front wheel + right rear wheel and right front wheel + left rear wheel. That is, when there is a breakdown or hydraulic leakage in one brake line, the diagonal front and rear wheels on the other brake line continue to be braked.
Operation of the Brake Central Pump in the Case of a Leak in the Brake System:
The brake hydraulic oil reservoir box above the brake center pump is also bipartite, so in case of leakage in one line, it is possible to supply hydraulic oil for the other line. There are also two pistons in the brake center pump, and when one line leaks, the other piston can generate pressure and the solid brake line continues to work.
(Main Brake Cylinder Operation in the Case of a Hydraulic Oil Leak)

